13. cp - cp command is used to copy the file from one
location to another.
Eg. touch test1
cp test1 testdir/test2
The above set of commands will first create an empty file
called test1. Then the file would be copied in another folder testdir and would
be saved with name test2.
we can see the files below:
The above screen print shows the touch command creating
test1 file.
The above screen shot shows the copy of test1 in testdir
folder and named as test2.
Please note that cp command is different from mv. If you use
mv instead of cp, a new file will not be created but rather the file would be
moved from one location to another.
14. ln - ln command is used to create links to a file. Links
can be of two types , soft link and hard link.
Lets create a hard link.
Eg.
In the above example we created an empty file called test1.
Then we created a hard link to test1 as test2 using ln command. When we checked
to contents of test1 and test2, both the files were empty. Then we added some
text to test1 and verified it using cat command. Later we verified the contents
of test2 using cat command. Note that the contents of test1 are also replicated
in test2. Note that, test2 is not the actual file and hence will always have
the size as 0 bytes as shown below.
In order to create soft links, we can use ln command with
-s.
Eg. ln -s test1 test1_soft
This will create a soft link named test1_soft for test1
file. It is shown below:
Now, if the original file test1 is deleted, the contents of
the hard link test2 will still remain but the soft link test1_soft will become
unusable.
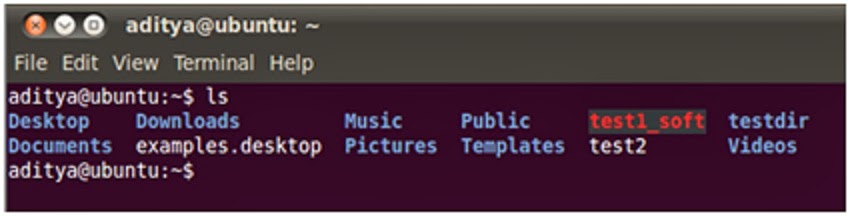
In above screenshot, test1 file is deleted however, a hard
link test2 and soft link test1_soft are still present.
If you try to see the data in a hard link, it is still
available.
However, when you try to see data in soft link, then error appears.








Awesomw stuff...... :)
ReplyDeleteWaiting for more tutorials :)